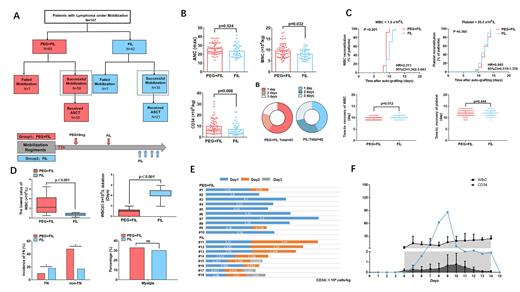
BACKGROUND : Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is broadly utilized for the treatment of lymphoma. Autologous peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) transplantation (ASCT) requires mobilization of hematopoietic stem cell/ hematopoietic progenitor cell (HSC/HPC) in peripheral blood (PB) to collect HSCs. The high mobilization failure rate with the mobilization strategy of combining chemotherapy and filgrastim (rhG-CSF, recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor) in ASCT is one of the unresolved issues. Whether the combination of polyethylene glycol filgrastim [pegfilgrastim (PEG-FIL), PEG-rhG-CSF] and filgrastim (FIL) improves the mobilization success rate and the timing of combination therapy has not been studied.
METHODS: To test the hypothesis that the combination of pegfilgrastim and filgrastim schedule has superiority, we retrospectively investigated a cohort of 107 lymphoma patients who received auto-HSCT and collection in the First Hospital of Jilin University from Jan 1st 2015 to Dec 1st 2022. These patients were categorized into PEG+FIL group and FIL group. The group of PEG+FIL received pegfilgrastim (9 mg) on the third day of the chemotherapy, followed by filgrastim (10 μg/kg/day) based on the counts of peripheral blood stem cells (PBSC). The group of FIL received filgrastim 10 μg /kg/day depending on the number PBSCs. Demographic information, laboratory results, and treatment plans were collected for these two groups of patients.
RESULTS:We compared their mobilization efficacy (mononuclear cell [MNC] and CD34 + cell counts) and transplantation efficacy (days to leukocyte and platelet recovery post-transplantation). Successful ASCT mobilization was achieved in 93 patients (86.9%), with the PEG+FIL group exhibiting a higher success rate compared to the FIL group (89.2% [58/65] vs. 83.3% [35/42], p = 0.032). The PEG+FIL group also demonstrated significantly higher CD34+ cell counts [MNC: 8.9 (6.9, 11.2) vs. 7.8 (6.2, 9.8) × 10 8 cells/kg, p = 0.024; CD34 + cell count: 7.5 (5.6, 13.0) vs. 4.9 (3.2, 9.2) × 10 6 cells/kg, p = 0.008] and a lower incidence of neutropenic fever compared to the FIL group (11.8% vs. 24.3%, p = 0.038). The PEG+FIL group also demonstrated a shorter mean leukocyte recovery time in autologous stem cell transplantation than the FIL group (10.02 ± 0.73 vs. 10.9 ± 1.1 days, p < 0.001).
To delve deeper into the safety considerations of both groups, we evaluated the advantages of each regimen and the methodologies for selecting time windows. A bone marrow aspiration and biopsy were performed on all patients before stem cell collection. Among 18 patients who had a hematopoietic area less than 30% and a fat area greater than 40%, 10 were in the PEG+FIL group and 8 in the FIL group. For patients who required only one collection, the durability was 80% in the PEG+FIL group compared to 0% in the FIL group (p < 0.01), indicating a superior recommendation for patients with a bone marrow hematopoietic area of less than 30%. In the PEG+FIL group, monitoring was carried out for PB CD34 + percentage and WBC count following pegfilgrastim administration, with subsequent computation of CD34 + cells in PB. Filgrastim administration was found to be optimal 5-6 days post-pegfilgrastim administration.
CONCLUSIONS: In conclusion, relative to conventional filgrastim mobilization, the conjunctive use of pegfilgrastim and filgrastim demonstrates superior efficacy, non-inferior safety during ASCT. The schedule enhanced the the outcomes of mobilization in the patients of less hematopoietic area.
KEY WORDS: Pegylated recombinant human granulocyte-stimulating factor (pegfilgrastim, PEG-rhG-CSF), recombinant human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (filgrastim, rhG-CSF), lymphoma, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) autologous hematopoietic stem cell mobilization.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.